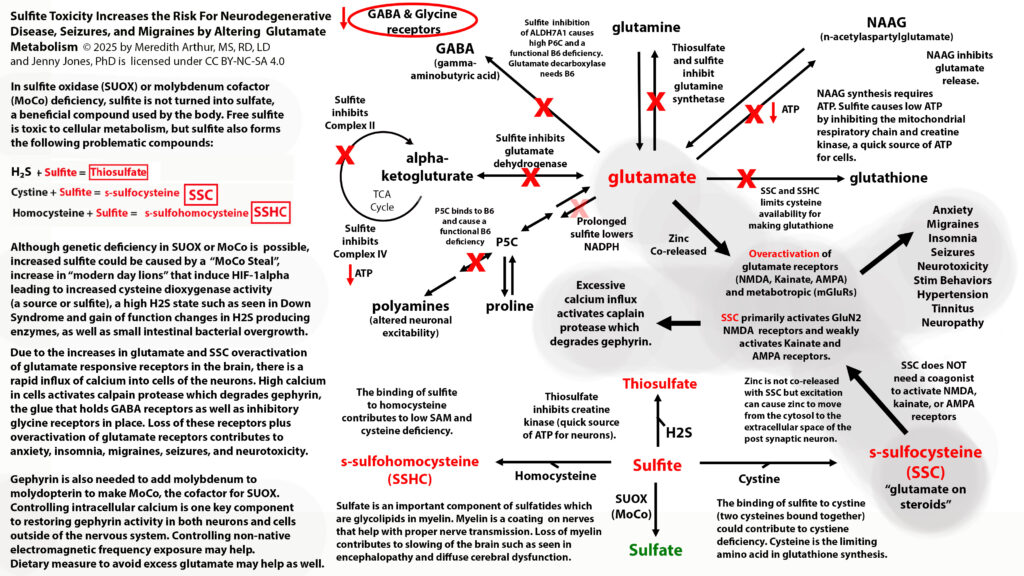
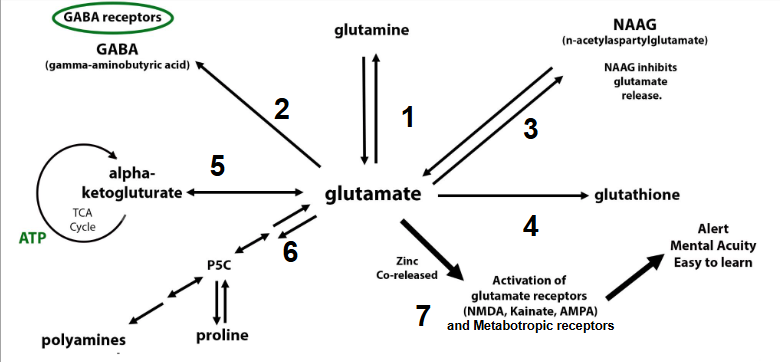
Sulfite toxicity in sulfite oxidase (SUOX) or molybdenum cofactor (MoCo) deficiency can lead to neurotoxicity due to the excessive production of s-sulfocysteine (SSC). It’s possible to have a genetic predisposition to decreased SUOX and/or MoCo. However, something to consider is that the current state of our environment can lead to what I like to call “endgame enzyme burnout”. Hypoxia, infections, and other “modern-day lions” can lead to increases in sulfite via the HIF-1alpha pathway induction of cysteine dioxygenase. Neutrophils produce sulfite in response to infections. As sulfite levels increase beyond the capacity of SUOX, sulfite alters glutamate metabolism and brain bioenergetics.
7 PATHWAYS FOR GLUTAMATE CAN ENTER
Neurones express glutamine synthetase when deprived of glutamine or interaction with astrocytes – PubMed Astrocytic Control of Biosynthesis and Turnover of the Neurotransmitters Glutamate and GABA – PubMed Glial Glutamine Homeostasis in Health and Disease – PubMed Neurones express glutamine synthetase when deprived of glutamine or interaction with astrocytes – PubMed Glial Glutamine Homeostasis in Health and Disease – PubMed
Disrupted de novo pyrimidine biosynthesis impairs adult hippocampal neurogenesis and cognition in pyridoxine-dependent epilepsy – PMC
Inactivation of gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase, but not of glutamine synthetase, by S-sulfocysteine and S-sulfohomocysteine.
Effects of Ingested Sulfite on Glutamate Synthesis and Release in the Rat Hippocampus | Neurochemical Journal
Inhibition of succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase activity by alkenal products of lipid peroxidation – ScienceDirect
Inhibition of GABA shunt enzymes’ activity by 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde derivatives – PubMed
Brain succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase: identification of reactive lysyl residues labeled with pyridoxal-5′-phosphate – PubMed
Volatile carbonylic compounds in downtown Santiago, Chile – PubMed
RIFM fragrance ingredient safety assessment, p-tolualdehyde, CAS Registry Number 104-87-0 – PubMed
Cysteine, sulfite, and glutamate toxicity: a cause of ALS? – PubMed
Sulfite Impairs Bioenergetics and Redox Status in Neonatal Rat Brain: Insights into the Early Neuropathophysiology of Isolated Sulfite Oxidase and Molybdenum Cofactor Deficiencies | Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology
Increased ROS levels, antioxidant defense disturbances and bioenergetic disruption induced by thiosulfate administration in the brain of neonatal rats – PubMed
Disturbance of brain energy and redox homeostasis provoked by sulfite and thiosulfate: potential pathomechanisms involved in the neuropathology of sulfite oxidase deficiency – PubMed
Astrocytes regulate inhibitory neurotransmission through GABA uptake, metabolism, and recycling | Essays in Biochemistry | Portland Press
GABAB receptor-mediated activation of astrocytes by gamma-hydroxybutyric acid
(PDF) Astrocytic Dysfunction and Addiction: Consequences of Impaired Glutamate Homeostasis
Frontiers | Disturbance of the Glutamate-Glutamine Cycle, Secondary to Hepatic Damage, Compromises Memory Function
Glutathione in the Brain – PMC
Sci-Hub | Disturbance of brain energy and redox homeostasis provoked by sulfite and thiosulfate: Potential pathomechanisms involved in the neuropathology of sulfite oxidase deficiency. Gene, 531(2), 191–198 | 10.1016/j.gene.2013.09.018
Disruption of Energy Transfer and Redox Status by Sulfite in Hippocampus, Striatum, and Cerebellum of Developing Rats – PubMed
Disruption of Energy Transfer and Redox Status by Sulfite in Hippocampus, Striatum, and Cerebellum of Developing Rats – PubMed
Evidence that Thiosulfate Inhibits Creatine Kinase Activity in Rat Striatum via Thiol Group Oxidation – PubMed
Increased ROS levels, antioxidant defense disturbances and bioenergetic disruption induced by thiosulfate administration in the brain of neonatal rats – PubMed
In vitro evidence that sulfite impairs glutamatergic neurotransmission and inhibits glutathione metabolism-related enzymes in rat cerebral cortex – PubMed
S-Sulfocysteine’s toxic effects on HT-22 cells are not triggered by glutamate receptors, nor do they involve apoptotic or genotoxicity mechanisms – PubMed
Loss of postsynaptic GABA(A) receptor clustering in gephyrin-deficient mice – PubMed
Gephyrin is critical for glycine receptor clustering but not for the formation of functional GABAergic synapses in hippocampal neurons – PubMed
Reduced synaptic clustering of GABA and glycine receptors in the retina of the gephyrin null mutant mouse – PubMed
Glycinergic and GABAergic synaptic transmission are differentially affected by gephyrin in spinal neurons – PubMed
Molecular basis of the γ-aminobutyric acid A receptor α3 subunit interaction with the clustering protein gephyrin – PubMed
Molecular basis of the alternative recruitment of GABA(A) versus glycine receptors through gephyrin – PubMed
Gephyrin, the enigmatic organizer at GABAergic synapses – PubMed
(PDF) Gephyrin: a central GABAergic synapse organizer
S-sulfocysteine/NMDA receptor–dependent signaling underlies neurodegeneration in molybdenum cofactor deficiency – PMC